Capture:
Go to the Capture Menu on your toolbar:

Select Options:
See the Options Interface:
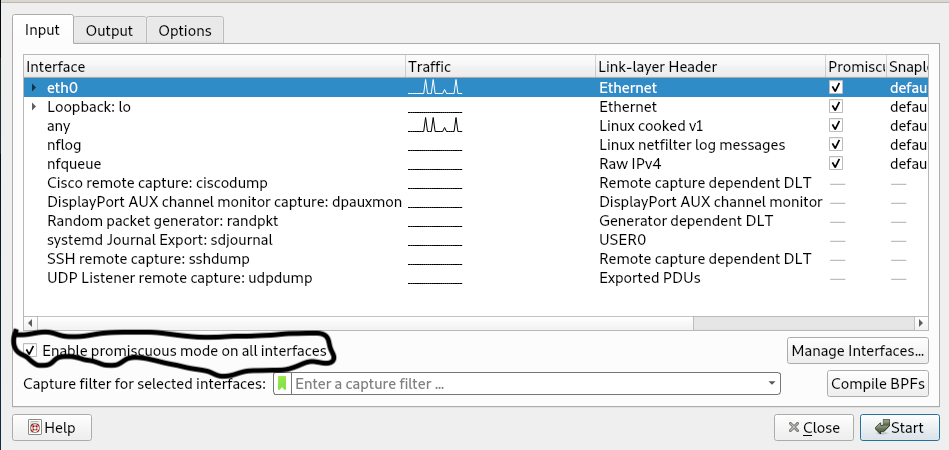
In order to listen to traffic from other sources (Make sure you have permission to do so) check to make sure Promiscuous mode is enabled:
Click the “Start” button
You can start seeing traffic being Captured:
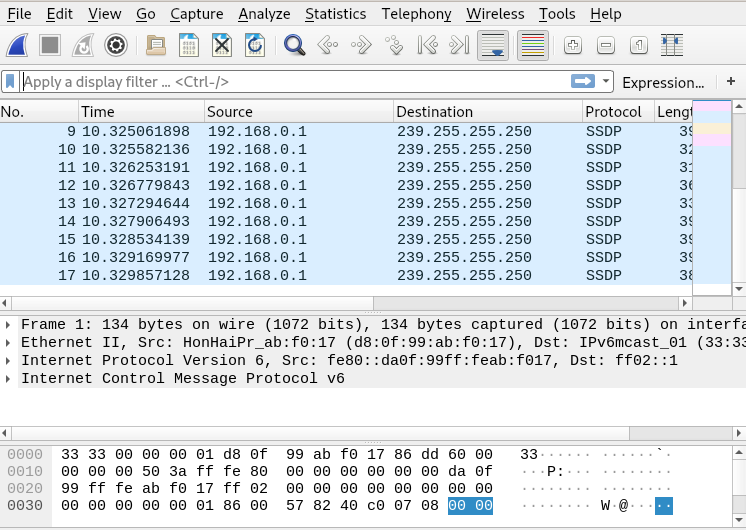
Look at the screen and see all of the icons:

Main toolbar items:

Checkout this page for more information: https://www.wireshark.org/docs/wsug_html_chunked/ChUseMainToolbarSection.html
Different Types of Filters:
- Display
- Capture
Display Filter:
The Display Filter can be found right under the Toolbar icons:

Capture Filter:
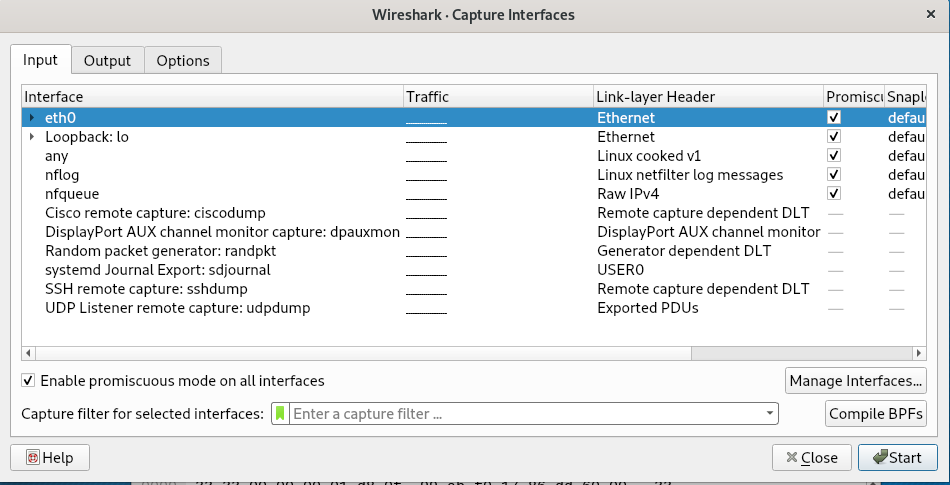
If you go to “Capture Options” either on the Toolbar or by clicking “Capture”:
The Capture Filters are right here:
How it works:
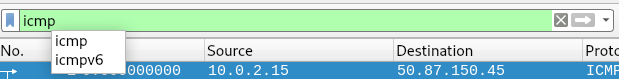
In the search bar you can type something to focus more of what you want.
For example I type ICMP and it will focus more of what I typed in the filter
Invalid Filter:
Indicated by being “Red”

Valid Filter:
Indicated by being “Green”
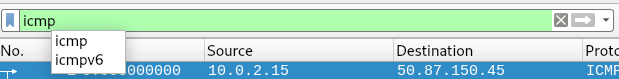
Filtering can get more combuersome,
For more information on how to use it go to:https://wiki.wireshark.org/DisplayFilters
What is a Packet?:
A package of information that you’re going to send to another computer.
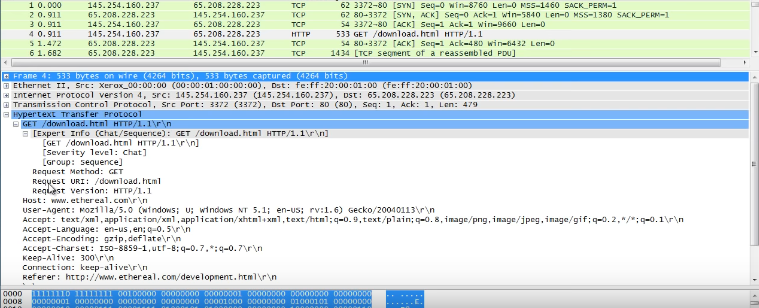
TCP:
IPV4:
This is the destination and return address information.
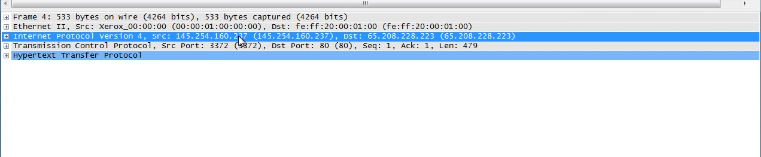
Ethernet:
Whenever your message is packaged up and ready to be sent, in this case you send to your router and then another router and eventually gets to where it needs to be.
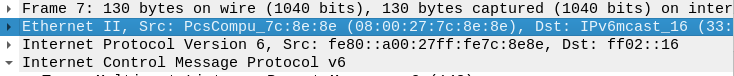
Frame:
The point where the software becomes real. Meaning the information that is 1s and 0s eventually get converted into meaningful information.
TCP Handshake:
SYN – SYN, ACK – ACK
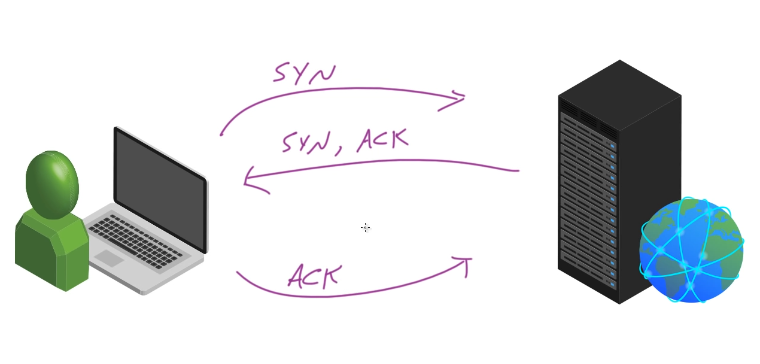
Wireshark Example:
SYN:
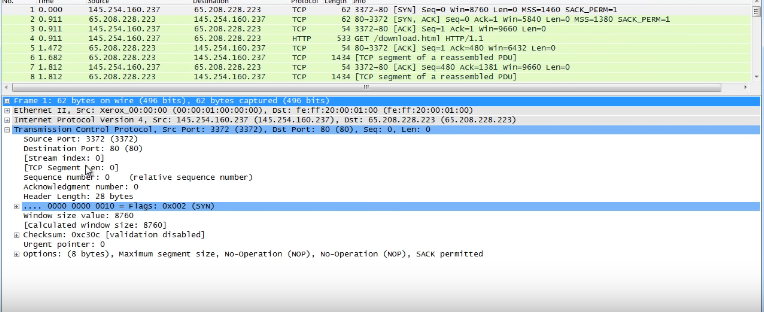
SYN, ACK:
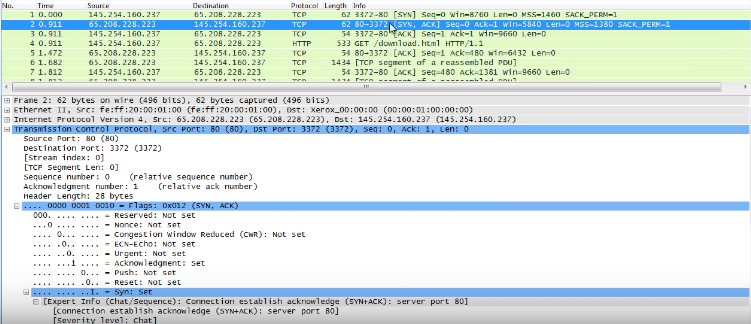
ACK:
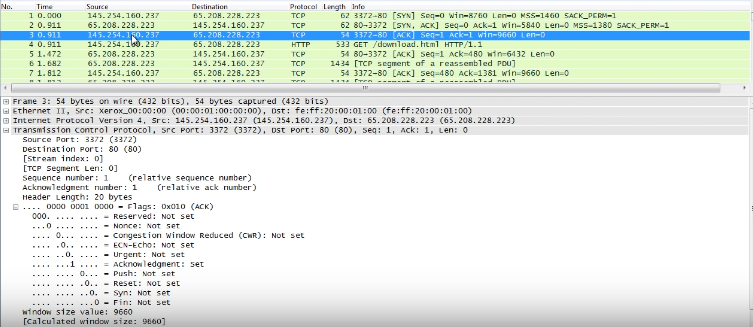
This is where the client heard the message from the server, and is sending back to server a notice that everything can proceed.
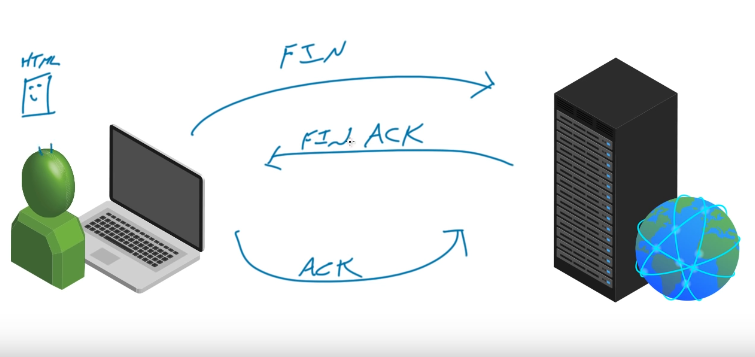
FIN – FIN , ACK -FIN:
Functions similiarly as above: